Everything you need to know about US quick commerce
5 minute read
What’s the deal with US quick commerce?

In a matter of months the rapid delivery grocery space has radically changed in America and elsewhere. Some of the highest cash burn rates ever have occurred in this industry, along with astronomic investment sums and rocketing valuations. Those valuations came plummeting back to earth in the last several months, along with acquisitions, layoffs, closures and major pivots.
In New York City alone, $800 million was pumped into qcomm companies in the last two years. The pandemic was a powerful catalyst for this sector, but now that lockdowns have ended, people have returned to in-store shopping. Add the present economic downturn and inflation into the mix, and it means one thing for this sector: no more cheap money.
Is US quick commerce doomed?
Not necessarily, but the frenetic change in this space has made for some uncertainty. It seems that too much money, too much freedom, and a flawed business model are to blame for a rocky start for qcomm.
Recently, the sector has seen everything from extending delivery times to ceasing delivery to selling logistics tech to delivering pharmaceuticals to making dark stores into hybrid walk-in shops. Phew. Basically, all the remaining players are looking for a new operational model that will enable them to survive.
The present US rapid grocery delivery market
The big question now is who’s left standing in this space, and who’ll be present six months from now? Here’s a quick rundown of the current status of the remaining players:


Fridge No More is no more (sorry) since March of this year. Buyk, after one year of operation, closed its doors at about the same time. In June Jokr pulled out of the US–after an injection of $430 million of venture capital. They lost 12 million in six months, losing $159 per order.


In late 2022, Getir acquired Gorillas for $1.2 billion. This was a major development in this space. Getir is a Turkish company with one of the first qcomm models and planned on expanding to New York, Boston and Chicago by the end of 2021. That didn’t happen as planned, but the acquisition of Gorillas makes that a partial reality.
Gorillas, a Berlin company, paused its US expansion in 2021, focusing on New York. They cut staff and had difficulties finding more funding, despite a $235 million US investment from Delivery Hero the same year. Before they were acquired, Gorillas extended delivery times from 10 minutes to an hour in some locations.

Instacart is now officially a player in the rapid delivery space. Already the leader in same day grocery delivery, it’s now working on its own service to bring customers their orders within 15 minutes. In May of this year, the company was forced to cut its valuation by nearly 40% to $24 billion. Seeking out new opportunities, Instacart is making a foray into health care delivery territory, along with Gopuff. At the time of writing Instacart has decreased its valuation to $13 billion.

The Instacart challenger
American DoorDash “connects consumers with their favorite local businesses”, “building infrastructure for local commerce”. Their service is not limited to instant grocery delivery but extends to companies like Big Lots, delivering home goods. DoorDash also has an express grocery delivery service with Kroger and Ahold Delhaize subsidiaries The Giant Company and Stop & Shop, putting them in direct competition with Instacart. Before the merger with Kroger, DoorDash announced a qcomm partnership with Albertsons.

The Champ?
Gopuff was valued at $15 billion in 2021. That valuation grew to $40 billion in January of this year, but by March, a planned IPO was no longer a reality, and its valuation had returned to $15 billion.
Gopuff reduced its workforce by more than 10% with two layoffs in 2022. It has closed dozens of dark stores and the founders claim they’re increasing investments into revenue-generating initiatives such as “commerce integrations and the tech behind Gopuff Ads.”
Despite all this, this American pioneer remains the favorite candidate for success for some observers. Their private label offering has had a fair bit of success, probably due to the products being high quality and having lower prices than established CPG products, and the company has now proved it has some staying power. In January of 2023 Gopuff partnered with Drizly for enhanced alcohol delivery.


Uber Eats and Deliveroo are not yet profitable but still standing. With a range of partnerships with retailers, their advertising platforms and assortment offerings enlarging, they’ve proven they may be able to stay in the game. Supermarkets are expanding their rapid grocery operations with both of these established players.
Two analyses illustrating weaknesses
in the qcomm model
One downside to the qcomm model and its dependence on small dark store locations is their restricted offering. Generally, a dark store carries around 2,000 products whereas a traditional grocer carries up to 60,000.
A limited assortment means limited opportunities for sales and repeat customers. Observers have raised the question of how many consumers really need a banana or a Snickers at 10pm at night in 10 minutes. If that potential market is small, a wider offering would be a boon to qcomm, but that doesn’t fit into their current business model.
This example shows how the limited product offering capacity of quick comm restricts new product introductions–which appeal to customers. The difference in new product introductions is limited at on-demand retailers like Gopuff as opposed to mainstream retailers.
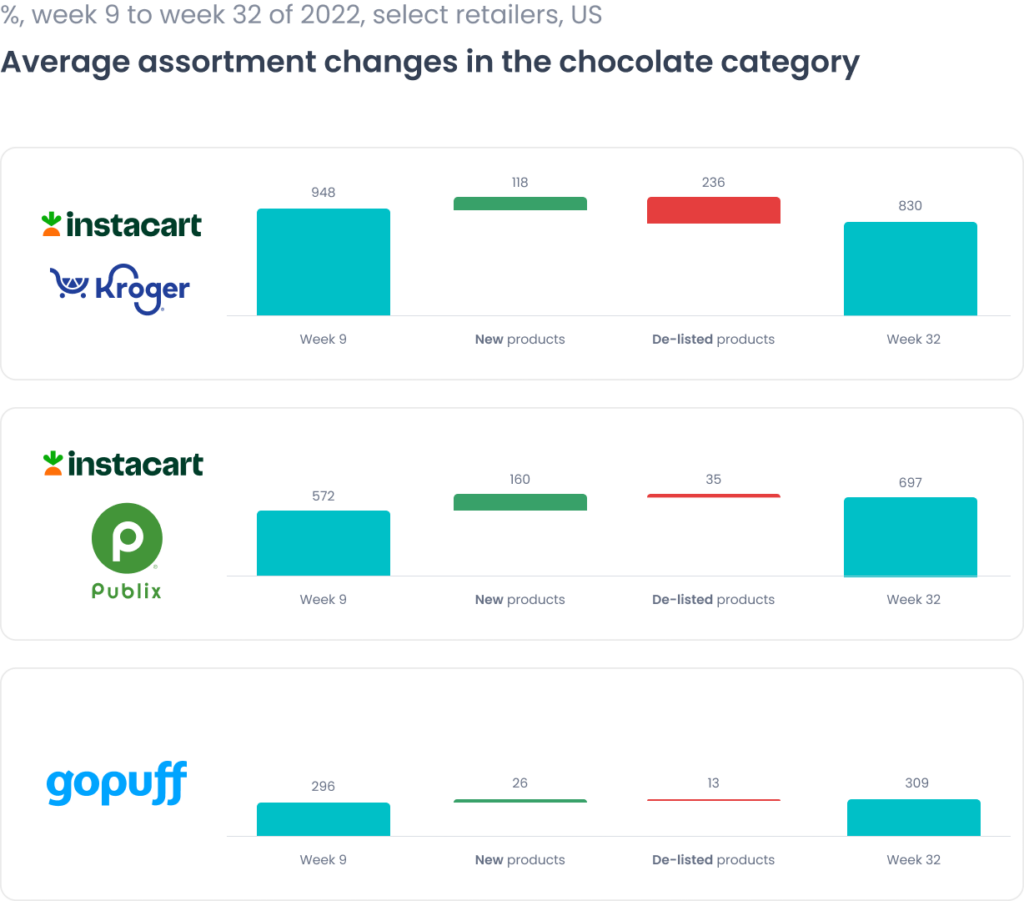
Also, since the qcomm offering is limited, there is more risk associated with out of stock products, because customers are turning to rapid delivery for specific items, and if they’re not in stock, customer loyalty is going to waver.
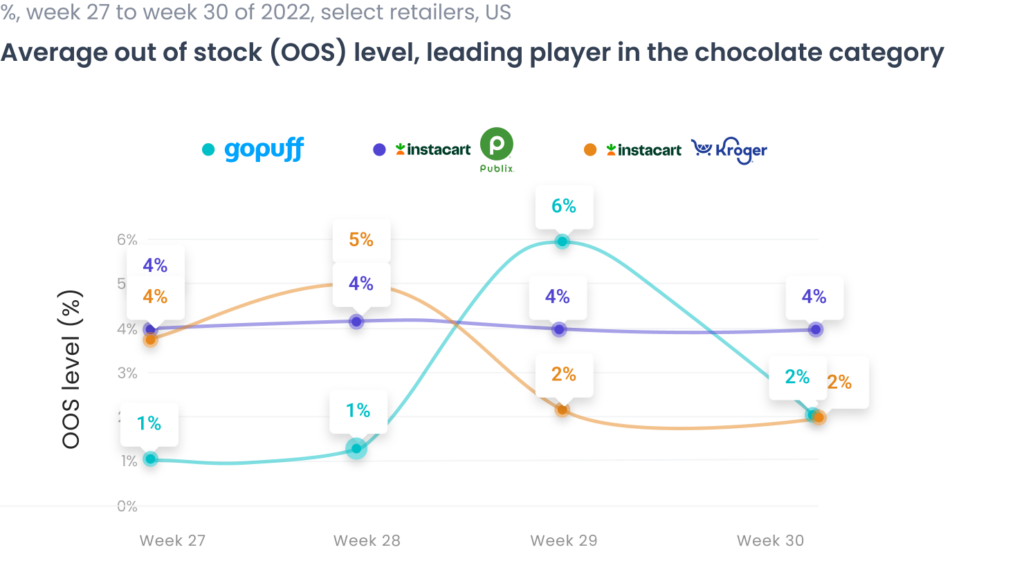
Second, quick comm companies have made a lot of noise about their superior logistics and inventory management tech, knowing how dangerous OOS can be for them. However, the reliability of that technology is debatable. The following analysis shows that OOS rates at Gopuff can spike when the OOS rates at traditional retailers don’t.
The future of quick commerce
The future for this sector is unclear. There are a number of pressures on quick comm companies right now. They include authorities regulating advertising for extraordinary delivery times, zoning laws preventing dark stores in urban areas and brick-and-mortar grocers launching 30-minute delivery services and adjusting their fees–thus encroaching on the qcomm space.
The revenue model remains an issue too. As cost-cutting drones, sidewalk robots and automated mini vehicles continue being tested by qcomm players, McKinsey recently stated that a typical mainstream retailer loses 13% on an online order. A qcomm order loses even more.
The rapid grocery delivery model will definitely have to evolve to survive. That said, the potential for it to do so is there. The pandemic has permanently altered consumer expectations and behaviors and now that Gen Zs and Millennials in particular have engaged with qcomm, an expectation for on-demand delivery has been established and isn’t likely to disappear.




